For 25 years, the Global Reporting Initiative has helped businesses and organizations take responsibility for their impacts by providing them with the world’s most widely used standards for sustainability reporting. This global common language allows organizations to report their impacts, enabling informed dialogue and decision-making.
The GRI was founded in Boston in 1997 following the public outcry that occurred after the Exxon Valdez oil spill. The organization wanted to ensure companies adhere to environmental conduct principles. These principles were later broadened to include social, economic, and governance issues.
The GRI Guidelines were published in 2000 to provide the first global framework for sustainability reporting. In 2001, GRI was established as an independent, non-profit institution.
In 2016, GRI transitioned away from guidelines to setting forth the first global standards for sustainability reporting: the GRI Standards.
What are the GRI Standards?
The GRI works with businesses, investors, policymakers, civil society, labor organizations, and more to develop, update, and add to the GRI Standards. The Standards enable any organization to credibly and transparently report their impacts on the economy, environment, and people. They are broken down into three series: the GRI Universal Standards, the GRI Sector Standards, and the GRI Topic Standards.
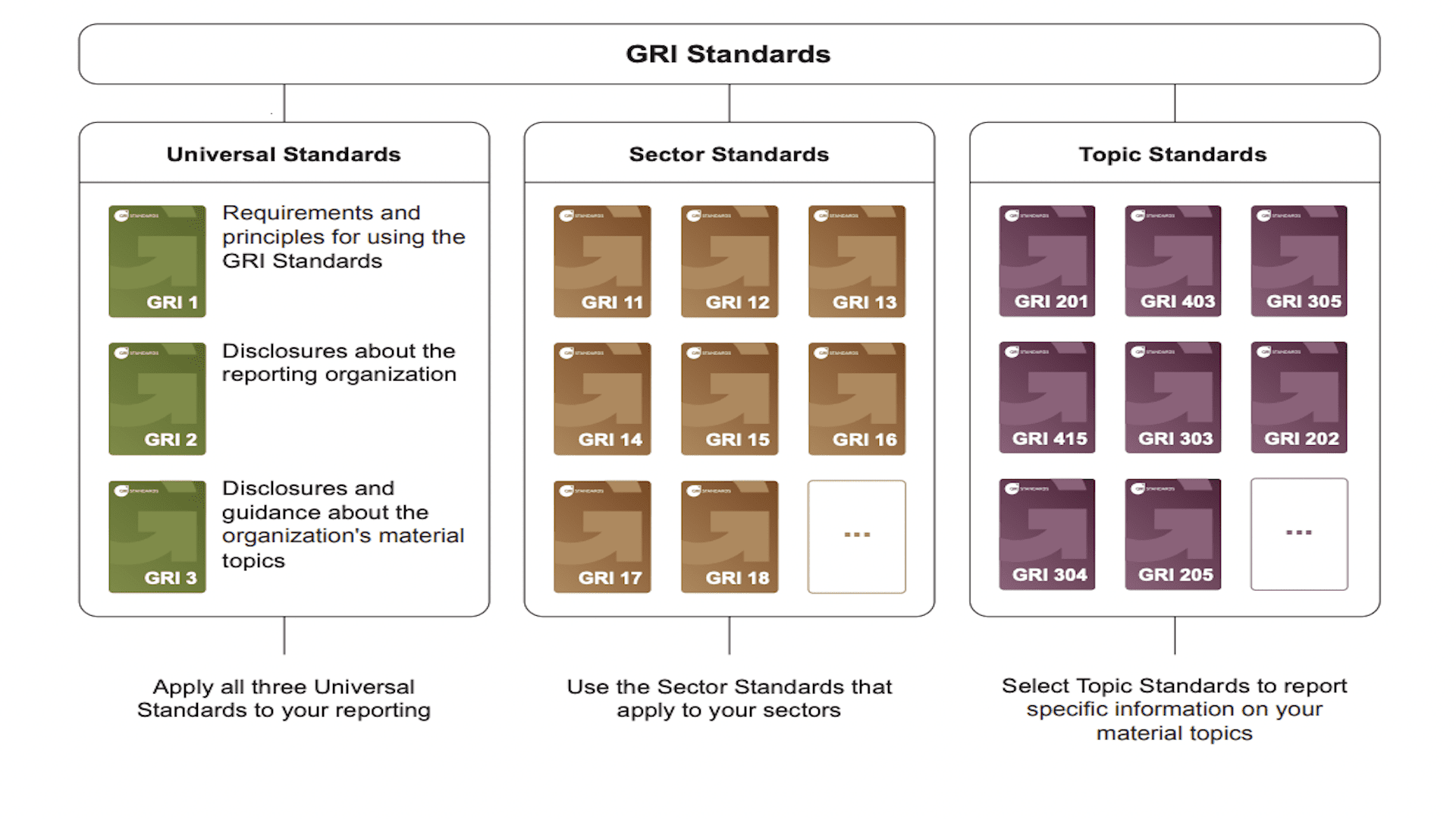
The GRI Universal Standards apply to all organizations. For example, every organization must comply with a certain number of requirements in terms of reporting, such as accuracy, balance, and verifiability.
Next, the GRI Sector Standards intend to increase the quality, competence, and consistency of reporting by developing different standards for 40 sectors. Each Sector Standard lists the overview of the sector’s characteristics, likely material topics, and additional disclosures. The sectors start with those of the highest impact, such as oil, gas, agriculture, and fishing.
Lastly, the GRI Topic Standards contain disclosures for providing information on certain topics. These topics include waste, occupational health and safety, and tax.
Examples of Organizations
Over 500 Organizations from over 70 countries are GRI Community Members. These organizations directly support GRI’s mission, are committed to corporate transparency, and cover a wide range of industries.
For example, the General Motors Company has been a GRI Community Member since 2003. In its 2021 Sustainability Report, the company says that the report “…has been prepared according to Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Standards: Comprehensive Option.” In the report, GM discloses its plans to be carbon neutral by 2040 and source 100 percent renewable energy at its sites in the United States by 2025.
Similarly, Johnson and Johnson is another GRI Community Member, and its 2021 Health for Humanity Report also cites GRI. This report includes statistics such as reducing CO2e emissions by 34 percent since 2016, spending $5.22 billion with small and diverse suppliers, and shipping 180 million doses of its COVID-19 vaccine to the African Union, COVAX, and South Africa.
Estée Lauder is also a GRI Community Member. In its Fiscal 2021 Social Impact and Sustainability Report, the company states “We map our priority focus areas to related Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Standards.” The report includes successes such as the company achieving Net Zero Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions and sourcing 100% renewable electricity globally for its direct operations.
For more of the latest news, check out the flooded mine that provides a scuba diving experience, an experiment that reveals the effects of nature on the brain, the fast repairs on the Sanibel Causeway, and the first U.S facility to turn plastic waste into concrete additive.